| |
| |
| Port Scanner |
 Download PortScanner
Download PortScanner
|
| |
|
There are various port scanners which uses simple method of
scanning. These applications uses the normal connect method to scan open
ports and it takes long time. This scanner is faster than normal scanner
as it uses faster 'TCP
Half Open' Scanning or 'TCP SYN' scanning technique. This method is less
detectable than the simple port scanner. |
| |
| |
|
When any two hosts wants to communicate together connection must be
established between them. In case of TCP connection, three way handshake takes
place between source and destination hosts. Below is the exact sequence
of packets exchanged between the hosts.
|
- First the source host A sends the SYN packet (TCP packet with SYN flag set) to host B.
- If the port is open then host B responds by sending SYN+ACK packet. else it
sends the RST+ACK packet to host B.
- Now host A sends the ACK packet to host B. (if SYN+ACK packet is received).
|
Once the connection is established,
both machines can transmit data packet until one of them ends the
connection by sending FIN packet. Some of the simple port scanners use
this technique. It can be implemented by creating socket and calling
'Connect method' on each port. This is simple to implement but very slow
method
and more over it can be easily detected. Half scanning is more fast and efficient than full
scanning technique. Half open connection is explained below.
|
- First the host A sends the SYN packet (TCP packet with SYN flag set) to host B.
- If the port is open then host B responds by sending SYN+ACK packet. else it
sends the RST+ACK packet to host B.
|
Since the host A does not send any additional ACK packet , it is called half
open connection. Now the host can easily find out if the target port is open or
closed. It it receives TCP packet with SYN+ACK flag set, then it means that
target port is open. If it receives RST+ACK packet, it implies that target port
is closed.
In this method full handshake does not take place ,
hence it is quite faster than full scanning method. Since the
implementation has to be done at the protocol level , knowledge of
TCP/IP protocol suite is essential.
|
| |
| |
|
Core part of the implementation is sending the TCP packet and ARP
packet. This involves building the raw packet by filling all headers.
For this we must know MAC address of the source and destination machine.
MAC address also called Ethernet address, is the address associated with
Ethernet adapter. |
| |
| |
|
| There are various methods for obtaining the source MAC address. This
method is simple. |
| |
IP_ADAPTER_INFO adapter[5];
DWORD buflen=sizeof(adapter);
DWORD status=GetAdaptersInfo(adapter,&buflen);
|
| Now the adapter structure contain the source MAC address. |
| |
| |
|
This is done by sending ARP packet. ARP packet is used to determine
the host's MAC address when its IP address is known. First ARP request
packet is sent by specifying the source MAC address, source IP address
and destination IP Address. The ARP reply packet contains the
destination MAC address. This method also prevents the target host from
sending ARP packet to source host when the source host sends the first
SYN packet during scanning process. From the ARP request packet that we
have sent, target host will come to know about the MAC address of the
source host. |
| |
| |
|
Scanning process involves building TCP packet. For
this one has to prepare the Ethernet Header, IP header and TCP header.
Header file 'packet.h' contains the format details for each of these
headers. You can refer RFC for details regarding these formats.
Each time during scanning TCP SYN packet is sent with
different port numbers. Then the corresponding reply packet is checked
for the flag RST+ACK or SYN+ACK. Based upon this flag target port status
is determined.
|
| |
| |
| |
 |
| |
| |
|
- All header files and libraries can be found in Winpcap developer pack 3.0 or
higher version. Don't forget to specify these 'include' and 'lib' paths
while building from the source code.
- For binary files such as winpcap.dll, install Winpcap 3.0 or higher
version.
|
| |
| |
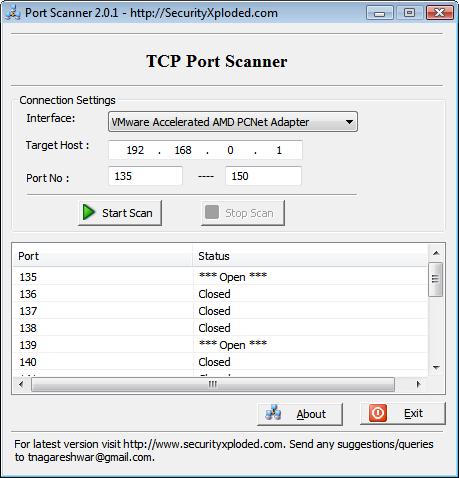
 PortScanner Version 2.0.1
PortScanner Version 2.0.1
|
|
Note: You need to download Winpcap to use this tool.
|
| |
| |
|
| Winpcap : Packet capture
library for Windows. |
| |
| |
|
| NetShareMonitor: Watch
your shares from intruders. |
| Changing the MAC address on your
computer. |
| ProcNetMonitor: Monitor
network activity of process. |
| RemoteDirDetector:
Remotely detect type of Directory server. |
| RemoteDLL: DLL
injection based tool to remove DLL from process. |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |